IP Subnet Hex to Bits
Overview
Convert IP address and subnet mask notation
In this example, IP 7.7.7.0 and mask FF.FF.FF.00 is converted to 7.7.7.0/24.
Supporting Concepts
Basic concepts needed for the use case
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| API | An API in API AutoFlow is simply an OpenAPI model |
| Server | A server accepts and handles the request and response. |
| Simulation | Data simulation is a mock data simulated for the purpose of visualizing the data in every step of the workflow.
|
| Scope | A scope is a namespace for variables. |
| Data Types | Data types describe the different types or kinds of data that you are gonna store and work with. |
Use case specific concepts
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Action object/get | Iterate over array of data mapping result to each array position. |
| Action string/join | Returns new string that joins the given Array into a string using 'delimiter'. |
Detail
The HTTP request has an input:
{
"address" : "7.7.7.0",
"mask" : "FF.FF.FF.00"
}
The goal of the operation is to convert the subnet mask bits to hex:
{
"address": "7.7.7.0/24"
}
Content
INPUT: HTTP Request
1: Create an API endpoint
Learn how to create an API.
Create an API
From the left navigation, go to the API section and create a new API.
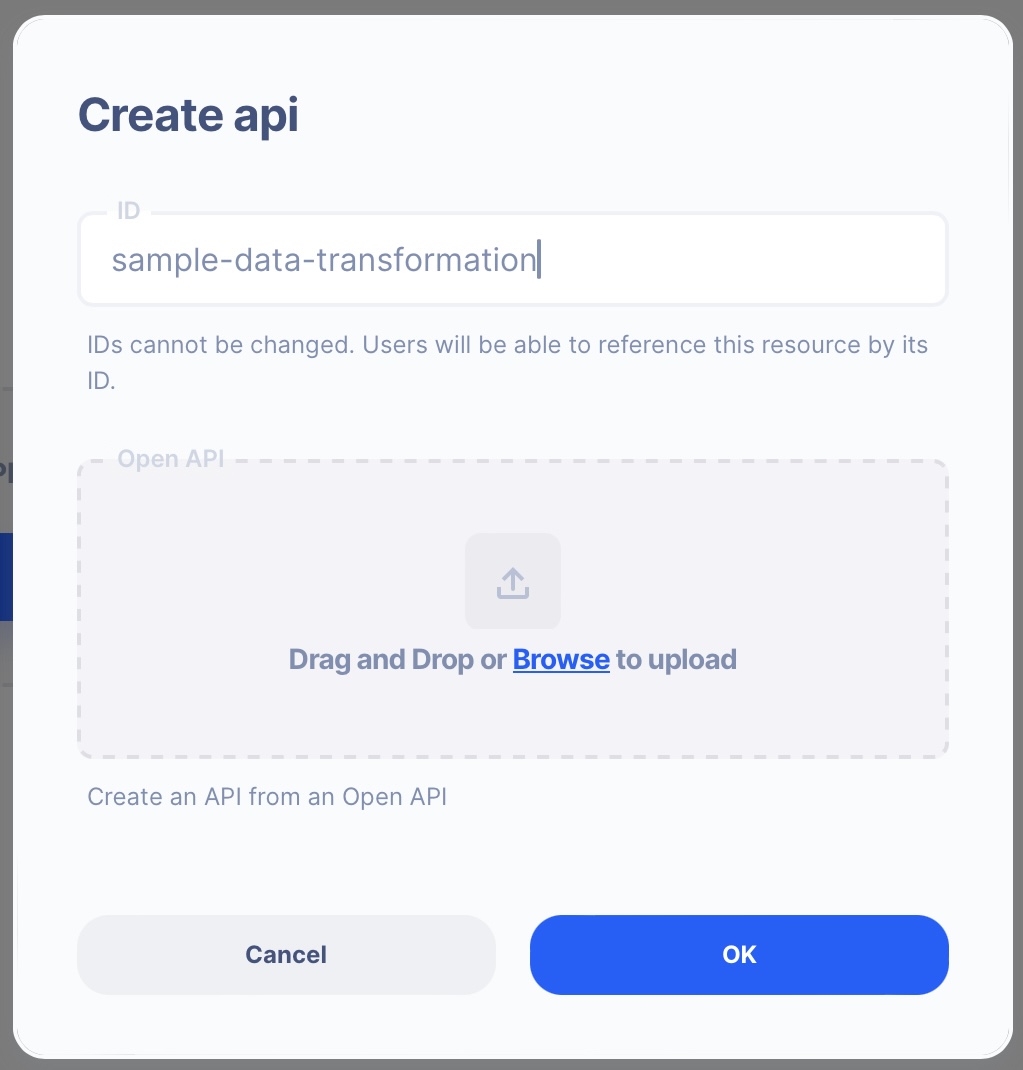
- ID:
sample-data-transformation
Create an API Path
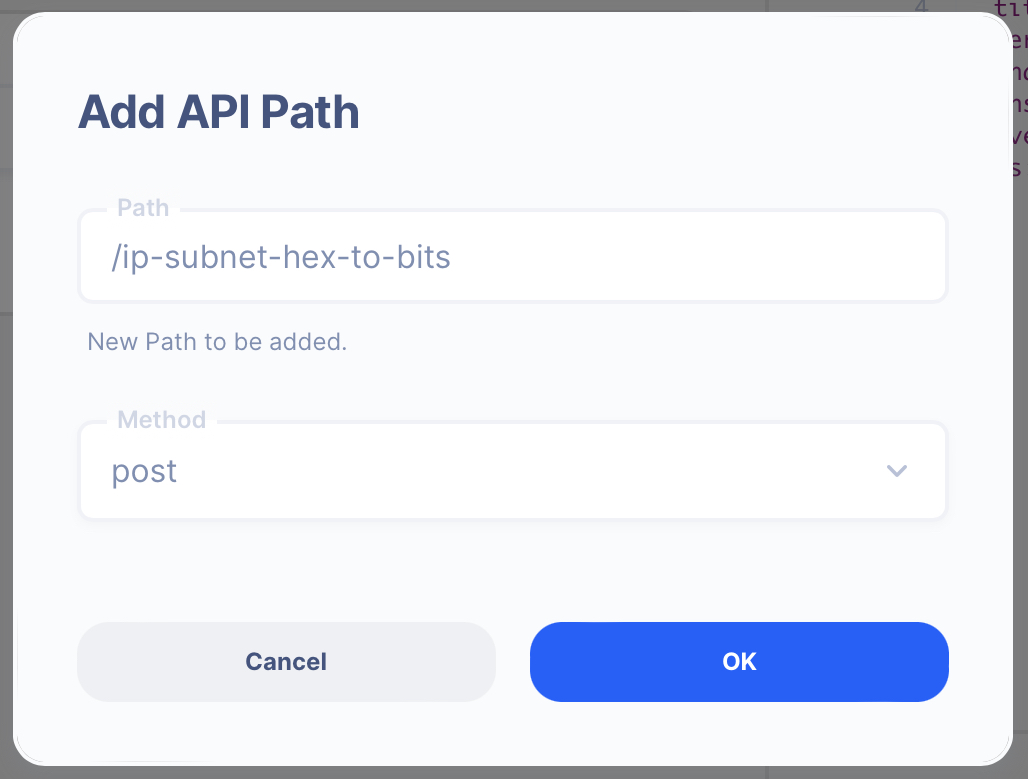
- Path:
/ip-subnet-hex-to-bits - Method: POST
2. Create a Server Operation
Learn how to create a Server.
Create a Server
From the left navigation, go to the Server section and create a new Server.
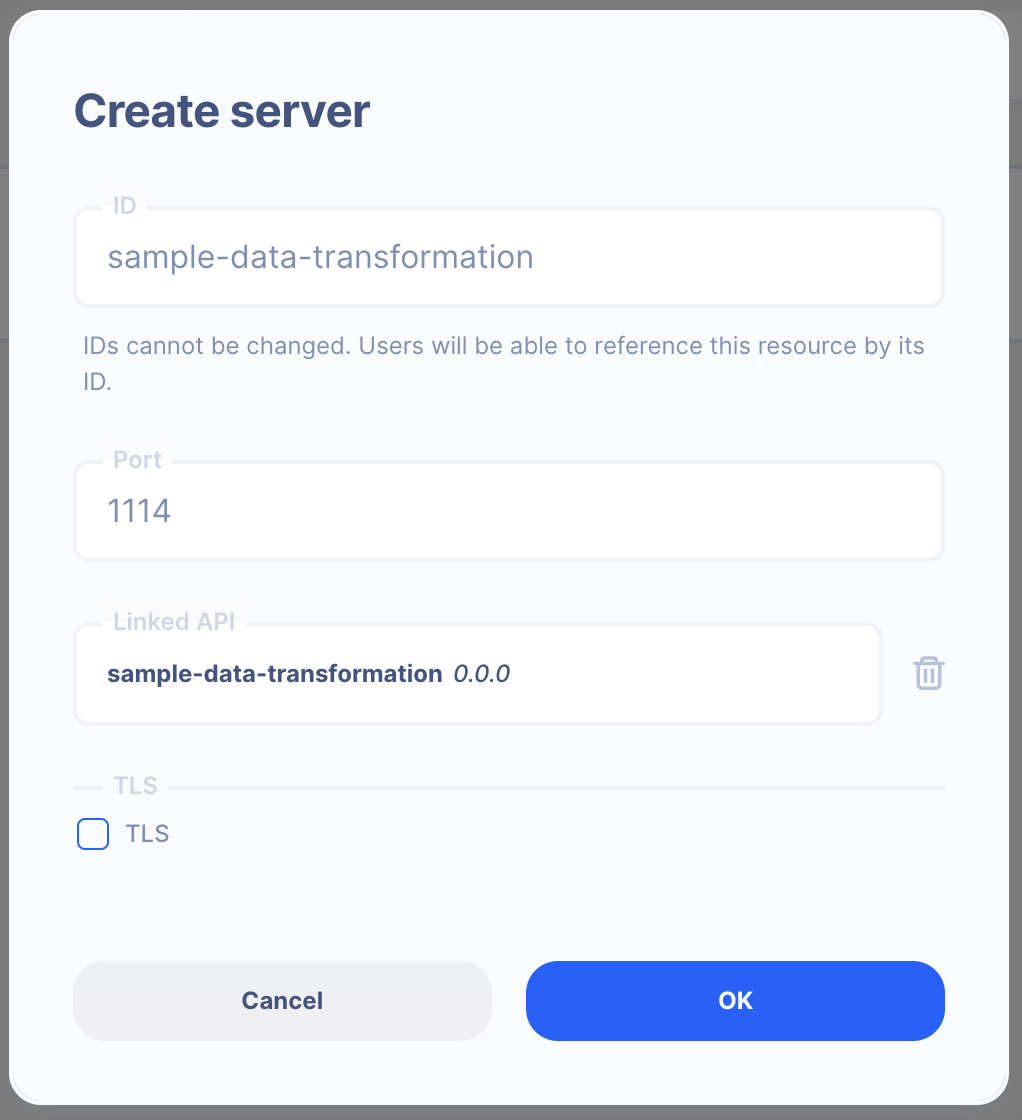
- Server ID:
sample-data-transformation - Port Number:
1114Feel free to select your own port number - Linked API:
sample-data-transformation(select the API you created above)
Create a Server Operation
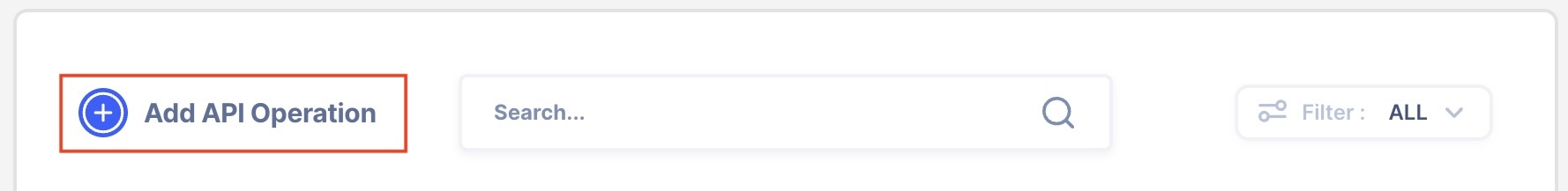
- Press the "Add API Operation"
- Select the API endpoint created above
3 : Create Data Simulation using Real Data
Learn how to create a Simulation.
We will use the "real data" to create the test simulation.
1. Send a HTTP request from Postman or CURL
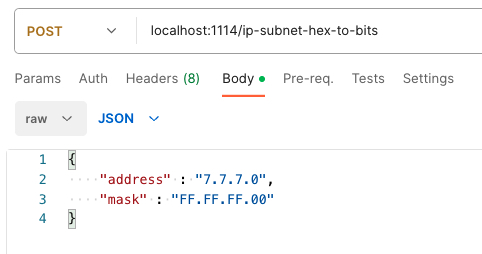
API Autoflow Postman Collections
cURL
curl --location 'localhost:1114/ip-subnet-hex-to-bits' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"address" : "7.7.7.0",
"mask" : "FF.FF.FF.00"
}'
2. Check the data is received by the server endpoint
API Autoflow captures the data received and it can be used to create data simulation.
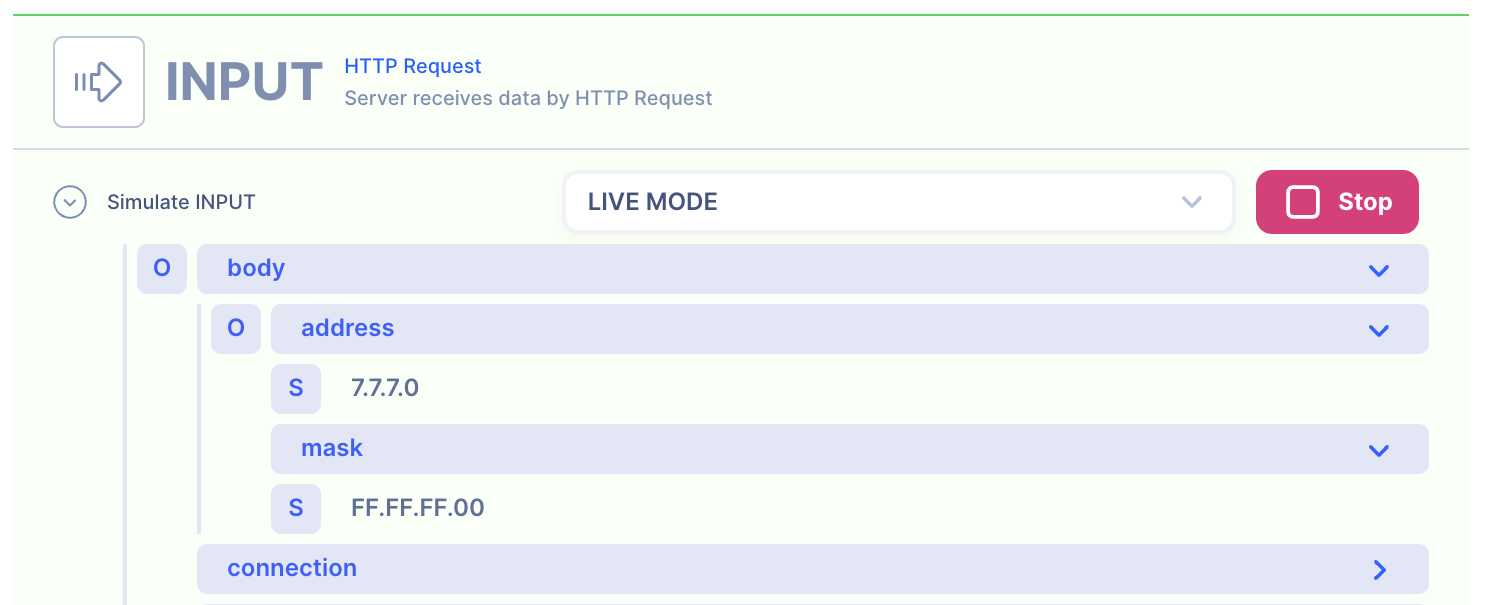
Action(s)
Learn how to create a Actions.
Add actions to transform the data.
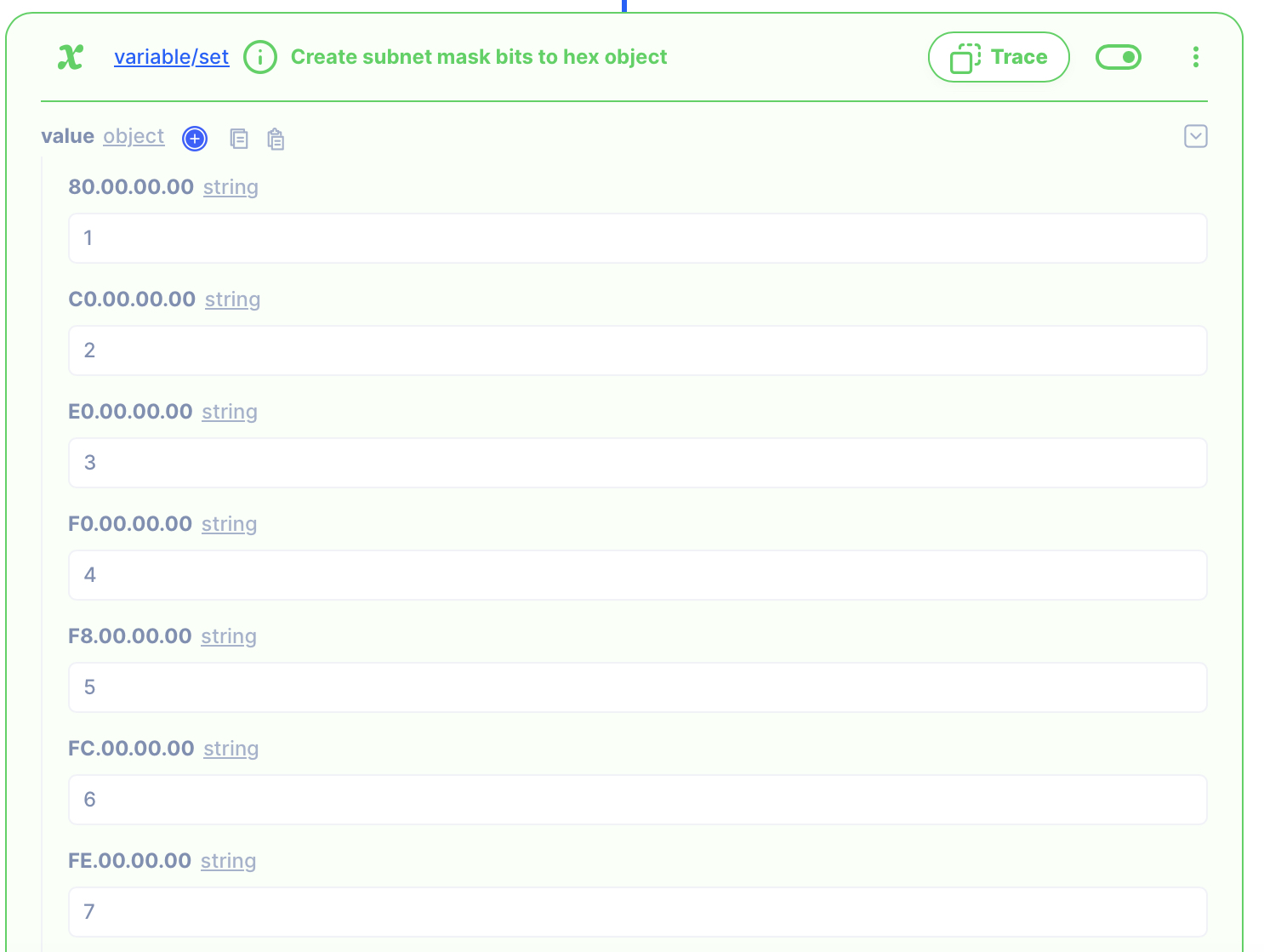
1. Create subnet mask bits to hex object
You can cut and paste the Bits to Hex object from the end of this document to the action's object.
Variable Set Action
2. Get the subnet mask bits value for the hex
From the bits to hex object, get the bits value that corresponds to the subnet mask hex value stored in variables: output.
Object Get
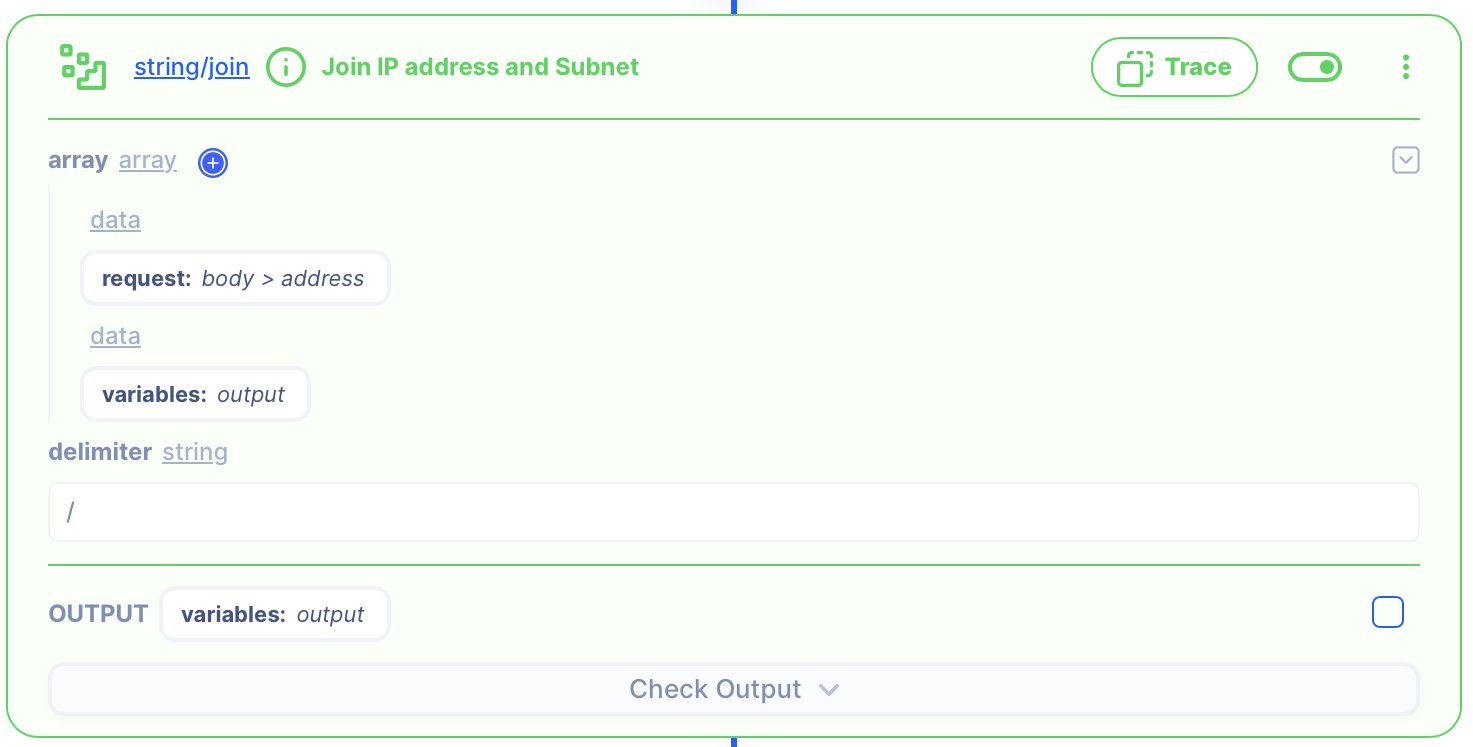
3. Join the IP address and subnet bits delimited by /
Put the IP and Subnet together.
String Join
OUTPUT: HTTP Response
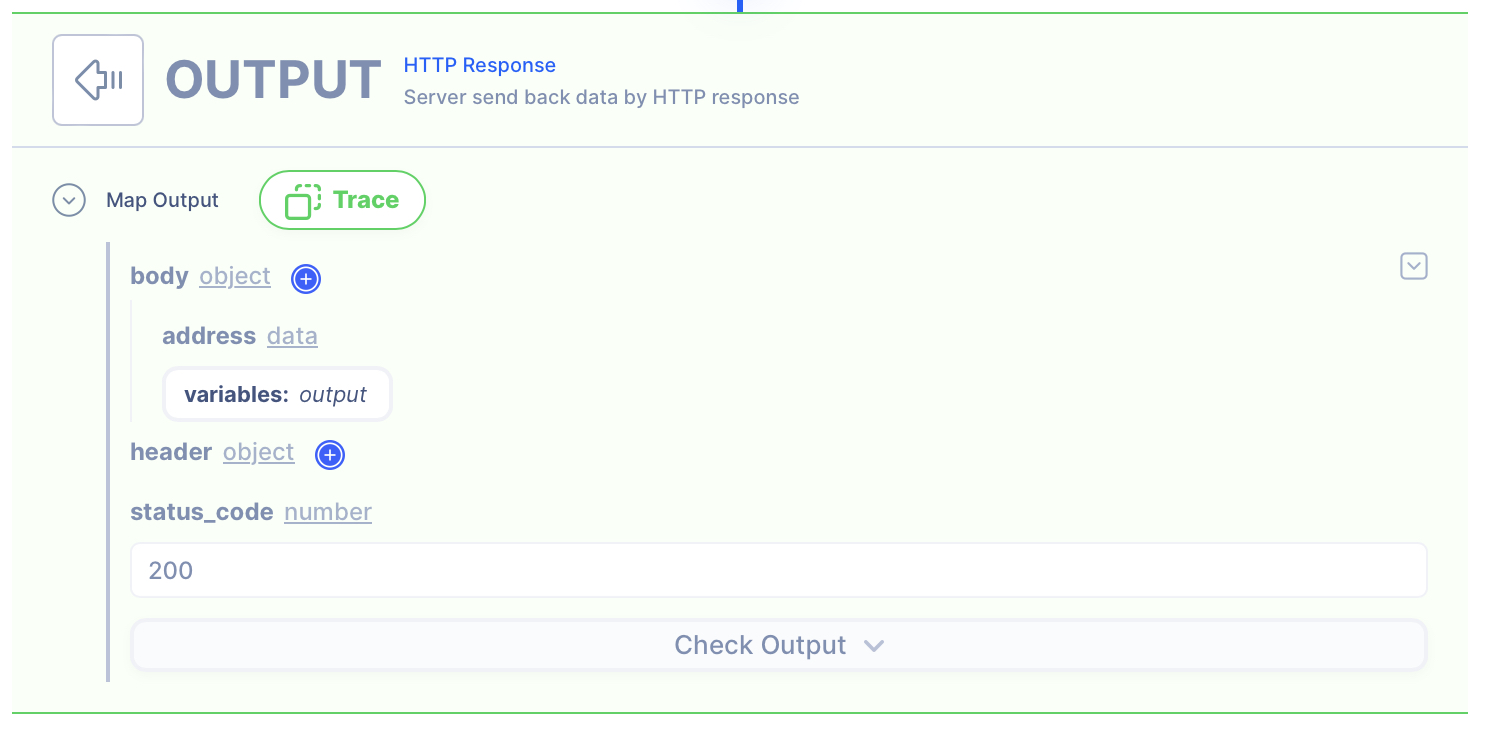
1. Create a NEW object and map the IP and Subnet
Since we need to respond in a JSON object, we can create a new object in the HTTP response.
- address: Getting it from the last actions' the variables:
output
HTTP Response
- Data referenced in HTTP response is what gets sent back to the client.
- Map the output from the actions to be sent back.
NOTE: By default, the action output is set to variable output. If you intend to keep each action's output without it being overwritten by the next action, simply rename the output location in the action's output.
2. Test the API with Postman or CURL
cURLcurl --location 'localhost:1114/ip-subnet-hex-to-bits' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"address" : "7.7.7.0",
"mask" : "FF.FF.FF.00"
}'
Bits to Hex table
{
"80.00.00.00": "1",
"C0.00.00.00": "2",
"E0.00.00.00": "3",
"F0.00.00.00": "4",
"F8.00.00.00": "5",
"FC.00.00.00": "6",
"FE.00.00.00": "7",
"FF.00.00.00": "8",
"FF.80.00.00": "9",
"FF.C0.00.00": "10",
"FF.E0.00.00": "11",
"FF.F0.00.00": "12",
"FF.F8.00.00": "13",
"FF.FC.00.00": "14",
"FF.FE.00.00": "15",
"FF.FF.00.00": "16",
"FF.FF.80.00": "17",
"FF.FF.C0.00": "18",
"FF.FF.E0.00": "19",
"FF.FF.F0.00": "20",
"FF.FF.F8.00": "21",
"FF.FF.FC.00": "22",
"FF.FF.FE.00": "23",
"FF.FF.FF.00": "24",
"FF.FF.FF.80": "25",
"FF.FF.FF.C0": "26",
"FF.FF.FF.E0": "27",
"FF.FF.FF.F0": "28",
"FF.FF.FF.F8": "29",
"FF.FF.FF.FC": "30",
"FF.FF.FF.FE": "31",
"FF.FF.FF.FF": "32"
}