CORS
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a security feature implemented by web browsers that controls how web pages in one domain can request and interact with resources (such as data or APIs) in another domain. The same-origin policy is a security measure implemented by web browsers to prevent web pages from making requests to a different domain than the one that served the web page. CORS provides a way to relax this restriction selectively.
When a web page hosted on one domain makes a request to a different domain (cross-origin request), the browser typically blocks the request by default for security reasons. CORS is a mechanism that allows a server to specify who can access its resources and under what conditions. It involves the server including specific HTTP headers in its responses that indicate which origins are permitted to access the resource.
The following are the main CORS headers:
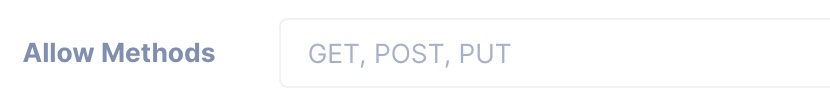
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: This header specifies the HTTP methods (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) that are allowed when accessing the resource.
Example
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, PUT
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: This header specifies which origins are allowed to access the resource. It can be a specific origin, a comma-separated list of origins, or the special value "*" (wildcard), which means that any origin is allowed.
Example
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://example.com

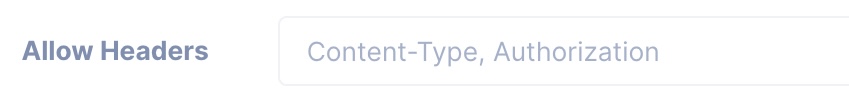
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: This header specifies the HTTP headers that can be used when making the actual request.
Example
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Authorization
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: This header indicates whether the browser should include credentials (e.g., cookies, HTTP authentication) when making the actual request. It can be "true" or "false."
Example
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true

CORS is a crucial aspect of securing web applications while allowing controlled access to resources across different origins. Properly configuring CORS headers on the server side is essential for enabling cross-origin requests in a secure manner.
Using the wildcard * in the Access-Control-Allow allows any request to access the resources on the server. While this can be convenient, it's important to note that using the wildcard may pose security risks if the server holds sensitive information or performs actions based on the received requests.