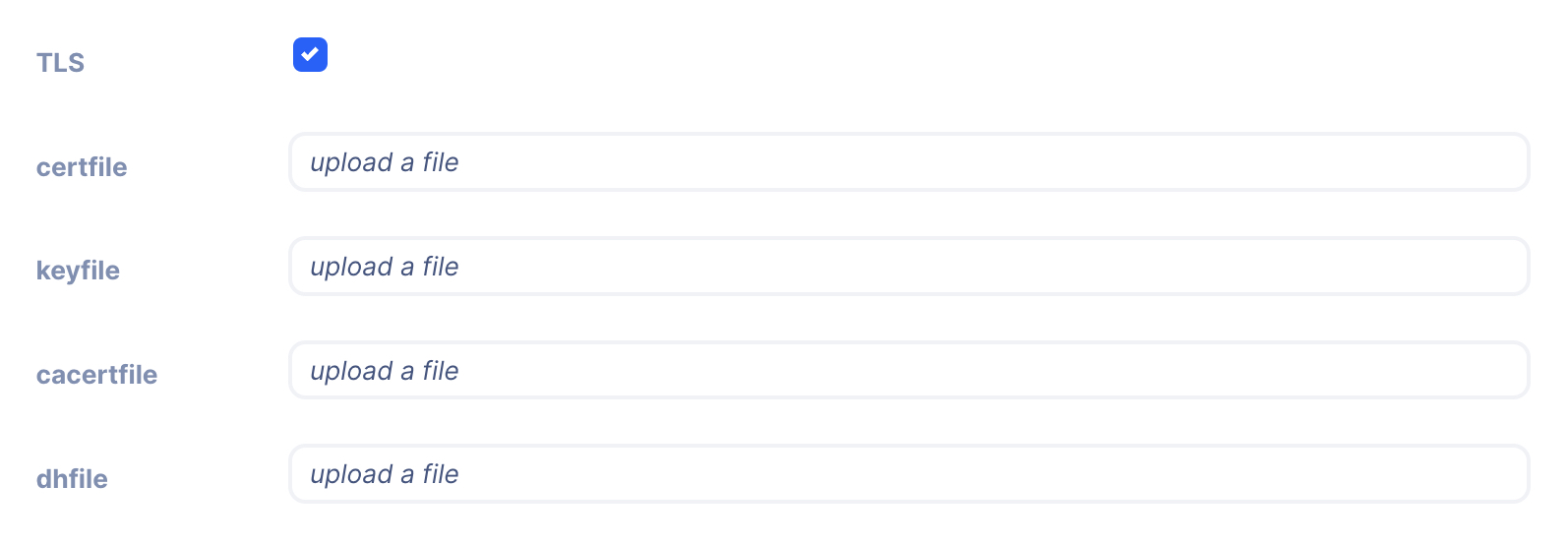
TLS
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide secure communication over a computer network. TLS is the successor to the older Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol. When you hear about websites using "HTTPS" (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), it means that they are using TLS to encrypt the data exchanged between the client (such as a web browser) and the server.
When working with TLS (Transport Layer Security) certificate files play a crucial role. These files are used to establish the authenticity of the communicating parties and to facilitate the encryption of data. The commonly used certification files in the context of TLS are:
- Server certificate:
server.crt - Private key:
server.key
When configuring a web server for TLS, you typically need to specify the paths to these certificate files. The server certificate and private key are mandatory, while the CA certificate and dh certificate are often required for creating a complete certificate chain.
Server Certificate:
certfile
File Extension: .crt, .pem, .cer
Purpose: This file contains the public key of the server. It is issued by a Certificate Authority and is presented by the server during the TLS handshake to prove its identity.
Example File Name:
server.crt
Private Key:
keyfile
File Extension: .key, .pem
Purpose: This file contains the private key corresponding to the public key in the server certificate. It is kept secret and is used by the server to decrypt messages encrypted with the public key.
Example File Name:
server.keyCertificate Authority (CA) Certificate :
cacertfile
File Extension: .crt, .pem, .cer
Purpose: This file contains the public key of a Certificate Authority. The CA certificate is used to verify the authenticity of other certificates in the certificate chain.
Example File Name:
ca.crt
Diffie-Hellman (DH) Certificate:
dhfile
File Extension: .crt, .pem
Purpose: The Diffie-Hellman parameters file, is used in the context of key exchange during the TLS handshake. The Diffie-Hellman key exchange is a method that allows two parties to agree upon a shared secret over an insecure communication channel
Example File Name:
dhparams.pem